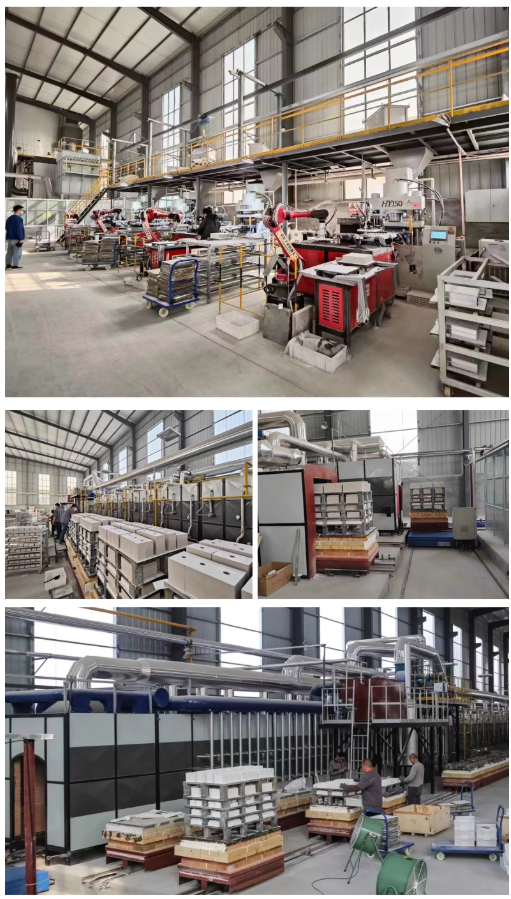
Professional Premium Aluminum Oxide Products Supplier
1. Introduction
In a development reported just yesterday by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), researchers have adopted alumina ceramic baking dishes for high-precision ash content analysis in next-generation battery materials. The shift stems from the dish’s ability to withstand repeated thermal cycling up to 1,700°C without warping or leaching contaminants—a critical requirement when analyzing trace elements in lithium-ion cathode powders.

Though many consumers recognize alumina ceramic baking dishes as elegant oven-safe cookware, their true potential lies in niche technical fields where purity, durability, and thermal resilience matter more than aesthetics. From metallurgy labs to aerospace material testing facilities, these unassuming vessels are quietly enabling breakthroughs.
2. Why Alumina Ceramic? The Science Behind the Material
Alumina (Al₂O₃) is a high-performance engineering ceramic known for its hardness, electrical insulation, and resistance to corrosion and thermal shock. When formed into dense, non-porous structures—like an alumina ceramic baking dish—it becomes chemically inert even when exposed to aggressive acids, molten metals, or oxidizing atmospheres.
Unlike standard stoneware or porcelain, which may contain fluxes or impurities that contaminate sensitive samples, high-purity (>99%) alumina ceramic dishes maintain integrity under extreme conditions. This makes them ideal not just for cooking, but for scientific workflows demanding reproducibility and cleanliness.
3. Real-World Application: Sample Evaporation and Ash Testing
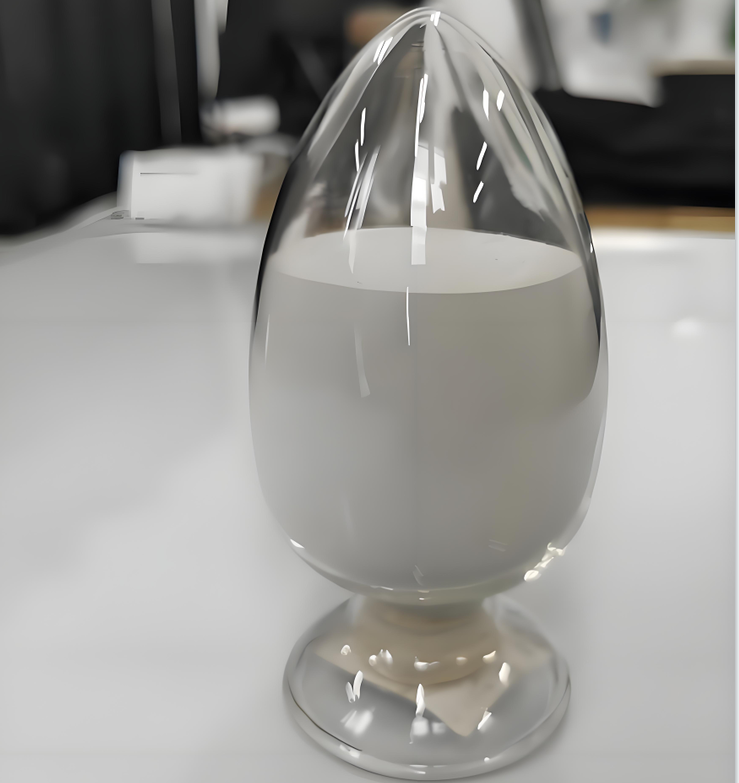

One of the most compelling niche uses of the alumina ceramic baking dish is in controlled evaporation and ash testing protocols. Environmental labs, for instance, use shallow alumina baking ceramic dishes to dry soil or water samples before elemental analysis. The flat geometry allows uniform heating, while the material prevents sodium or silica migration that could skew ICP-MS results.
Similarly, food safety laboratories employ alumina ceramic casserole dishes with lids to determine fat-free dry matter in dairy products. Because the alumina butter ceramic dish doesn’t absorb organic residues, cross-contamination between batches is virtually eliminated—something plastic or glass alternatives can’t guarantee at high temperatures.
4. Beyond the Oven: Integration with Advanced Lab Workflows
Interestingly, some researchers repurpose alumina ceramic serving platters and large alumina ceramic plates for painting as custom substrate holders during thin-film deposition. Their smooth, non-reactive surfaces provide stable platforms for coating trials without interfering with adhesion or crystallization.

Even small-format items like alumina ceramic ramekins and alumina ceramic sugar dishes find roles as micro-reactors for sol-gel synthesis. Their compact size and thermal uniformity allow precise control over nucleation in ceramic nanoparticle production.
5. Compatibility with High-Temperature Equipment
The same properties that make alumina ceramic dishes suitable for home ovens also enable seamless integration into industrial and research-grade equipment. An alumina oven ceramic dish can be placed directly into muffle furnaces, tube furnaces, or even inside alumina ceramic tubes for in-situ reactions.
- Alumina ceramic casserole with lid pairs well with alumina thermocouple protection tubes for real-time temperature monitoring during calcination.
- Shallow alumina salad ceramic bowls are used as catchment trays beneath alumina porous ceramic tubes during filtration experiments.
- Alumina ceramic plates black or white variants serve as calibration standards in optical pyrometry due to consistent emissivity.
6. Practical Considerations for Lab Use
When sourcing lab-grade alumina ceramic dishes, researchers prioritize fully vitrified, non-glazed versions to avoid hidden contaminants. While consumer products like alumina baking dish staub offer aesthetic appeal, technical applications demand specifications aligned with ASTM C704 or ISO 1893 standards.
Reputable suppliers now list alumina ceramic dishes for oven use with certified purity levels, maximum service temperatures, and thermal expansion coefficients—critical data for method validation. Some even offer custom geometries, such as alumina ceramic plate bowls with tapered edges for easy powder recovery.
7. Conclusion
The humble alumina ceramic baking dish has transcended its culinary origins to become a versatile tool in advanced scientific settings. Whether used as an evaporation vessel, ashing pan, or micro-reactor, its unmatched combination of purity, stability, and heat resistance ensures accuracy in high-stakes analytical procedures. As material science pushes toward cleaner, more precise methodologies, expect to see more labs swapping conventional glassware for purpose-built alumina ceramic dishes—from dinner plates to diamond-grinding-compatible crucibles.
Our Website founded on October 17, 2012, is a high-tech enterprise committed to the research and development, production, processing, sales and technical services of ceramic relative materials such as Alumina. Our products includes but not limited to Boron Carbide Ceramic Products, Boron Nitride Ceramic Products, Silicon Carbide Ceramic Products, Silicon Nitride Ceramic Products, Zirconium Dioxide Ceramic Products, etc. If you are interested, please feel free to contact us.